FAQ - Features - Inventory Management
Mapping, Merging, Matching, Pairing, and Linking - What do each of those mean and how are they related or different from each other?
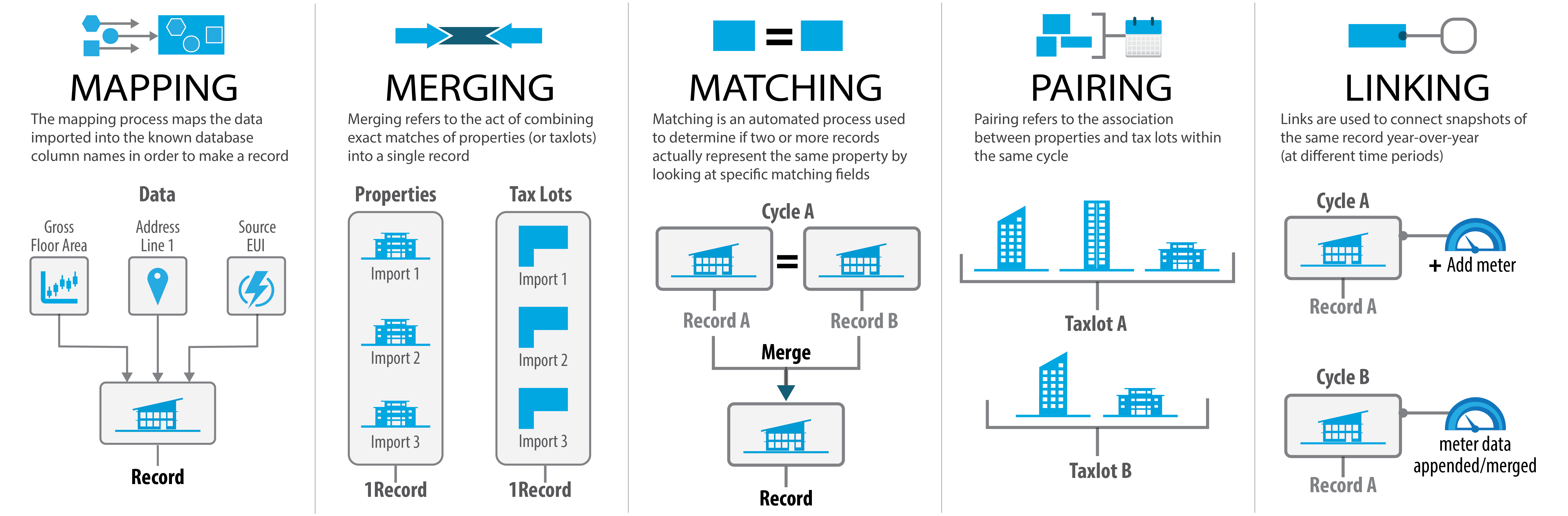
Different inventory management and analysis features in SEED are based on the relationships between records of different inventory types (properties and tax lots). Those terms help describe these relationships.
-
Mapping refers to the process of mapping newly imported data fields to the known database column names in order to create a record.
-
Merging refers to the act of combining multiple properties (or multiple tax lots) into one record. This can be done manually by users or automatically by SEED and helps avoid duplicate records.
-
Matching refers to whether two or more properties match (or two or more tax lots). A match can only happen if specific fields between records match. Records can be compared within the same cycle (triggering a merge) or across cycles (building a link). The specific fields can be modified for each organization.
-
Pairing refers to the association between properties and tax lots within the same cycle.
-
Linking refers to the association between properties across cycles (or tax lots across cycles) and is useful for analysis.
For more details, refer to this documentation that covers matching, merging, and linking.
The linking feature is new - can I get more details on how it works?
Cross-cycle linking, or simply linking, allows organizations to analyze uploads of the same property (or tax lot) over time. This is done by matching records in one cycle with records within other cycles. SEED builds these associations automatically during import using matching criteria as specified by the organization. Additionally, this association can be made during a manual edit to record values (especially if the changed value is a matching criteria field).
For even more details on matching and linking, refer to this section of the matching, merging, and linking documentation.
How does linking interact with paired properties and tax lots?
At the moment, paired property and tax lot relationships are displayed and managed separately from linked relationships. That is, paired records are viewed and managed in a separate area of SEED as linked records.